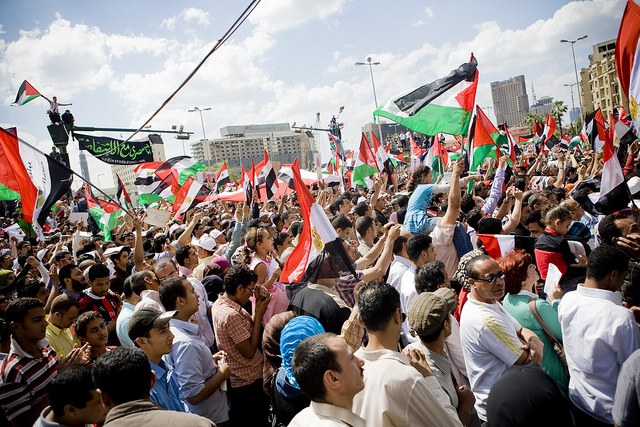
The communication technologies once used by rebels and protesters to gain global visibility now look burdensome and dated: much separates the once-futuristic-looking image of Subcomandante Marcos posing in the Chiapas jungle draped in electronic gear (1994) from the uprisings of the 2011 Egyptian revolution. While the only practical platform for amplifying a message was once provided by organisations, the rise of the Internet means that cross-national networks are now reachable by individuals—who are able to bypass organisations, ditch membership dues, and embrace self-organization. As social media and mobile applications increasingly blur the distinction between public and private, ordinary citizens are becoming crucial nodes in the contemporary protest network.
The personal networks that are the main channels of information flow in sites such as Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn mean that we don’t need to actively seek out particular information; it can be served to us with no more effort than that of maintaining a connection with our contacts. News, opinions, and calls for justice are now shared and forwarded by our friends—and their friends—in a constant churn of information, all attached to familiar names and faces. Given we are more likely to pass on information if the source belongs to our social circle, this has had an important impact on the information environment within which protest movements are initiated and develop.
Mobile connectivity is also important for understanding contemporary protest, given that the ubiquitous streams of synchronous information we access anywhere are shortening our reaction times. This is important, as the evolution of mass recruitments—whether they result in flash mobilisations, slow burns, or simply damp squibs—can only be properly understood if we have a handle on the distribution of reaction times within a population. The increasing integration of the mainstream media into our personal networks is also important, given that online networks (and independent platforms like Indymedia) are not the clear-cut alternative to corporate media they once were. We can now write on the walls or feeds of mainstream media outlets, creating two-way communication channels and public discussion.
Online petitions have also transformed political protest; lower information diffusion costs mean that support (and signatures) can be scaled up much faster. These petitions provide a mine of information for researchers interested in what makes protests succeed or fail. The study of cascading behaviour in online networks suggests that most chain reactions fail quickly, and most petitions don’t gather that much attention anyway. While large cascades tend to start at the core of networks, network centrality is not always a guarantor of success.
So what does a successful cascade look like? Work by Duncan Watts has shown that the vast majority of cascades are small and simple, terminating within one degree of an initial adopting ‘seed.’ Research has also shown that adoptions resulting from chains of referrals are extremely rare; even for the largest cascades observed, the bulk of adoptions often took place within one degree of a few dominant individuals. Conversely, research on the spreading dynamics of a petition organised in opposition to the 2002-2003 Iraq war showed a narrow but very deep tree-like distribution, progressing through many steps and complex paths. The deepness and narrowness of the observed diffusion tree meant that it was fragile—and easily broken at any of the levels required for further distribution. Chain reactions are only successful with the right alignment of factors, and this becomes more likely as more attempts are launched. The rise of social media means that there are now more attempts.
One consequence of these—very recent—developments is the blurring of the public and the private. A significant portion of political information shared online travels through networks that are not necessarily political, but that can be activated for political purposes as circumstances arise. Online protest networks are decentralised structures that pull together local sources of information and create efficient channels for a potentially global diffusion, but they replicate the recruitment dynamics that operated in social networks prior to the emergence of the Internet.
The wave of protests seen in 2011—including the Arab Spring, the Spanish Indignados, and the Global Occupy Campaign—reflects this global interdependence of localised, personal networks, with protest movements emerging spontaneously from the individual actions of many thousands (or millions) of networked users. Political protest movements are seldom stable and fixed organisational structures, and online networks are inherently suited to channeling this fluid commitment and identity. However, systematic research to uncover the bridges and precise network mechanisms that facilitate cross-border diffusion is still lacking. Decentralized networks facilitate mobilisations of unprecedented reach and speed—but are actually not very good at maintaining momentum, or creating particularly stable structures. For this, traditional organisations are still relevant, even while they struggle to maintain a critical mass.
The general failure of traditional organisations to harness the power of these personal networks results from their complex structure, which complicates any attempts at prediction, planning, and engineering. Mobilization paths are difficult to predict because they depend on the right alignment of conditions on different levels—from the local information contexts of individuals who initiate or sustain diffusion chains, to the global assembly of separate diffusion branches. The networked chain reactions that result as people jump onto bandwagons follow complex paths; furthermore, the cumulative effects of these individual actions within the network are not linear, due to feedback mechanisms that can cause sudden changes and flips in mobilisation dynamics, such as exponential growth.
Of course, protest movements are not created by social media technologies; they provide just one mechanism by which a movement can emerge, given the right social, economic, and historical circumstances. We therefore need to focus less on the specific technologies and more on how they are used if we are to explain why most mobilisations fail, but some succeed. Technology is just a part of the story—and today’s Twitter accounts will soon look as dated as the electronic gizmos used by the Zapatistas in the Chiapas jungle.